

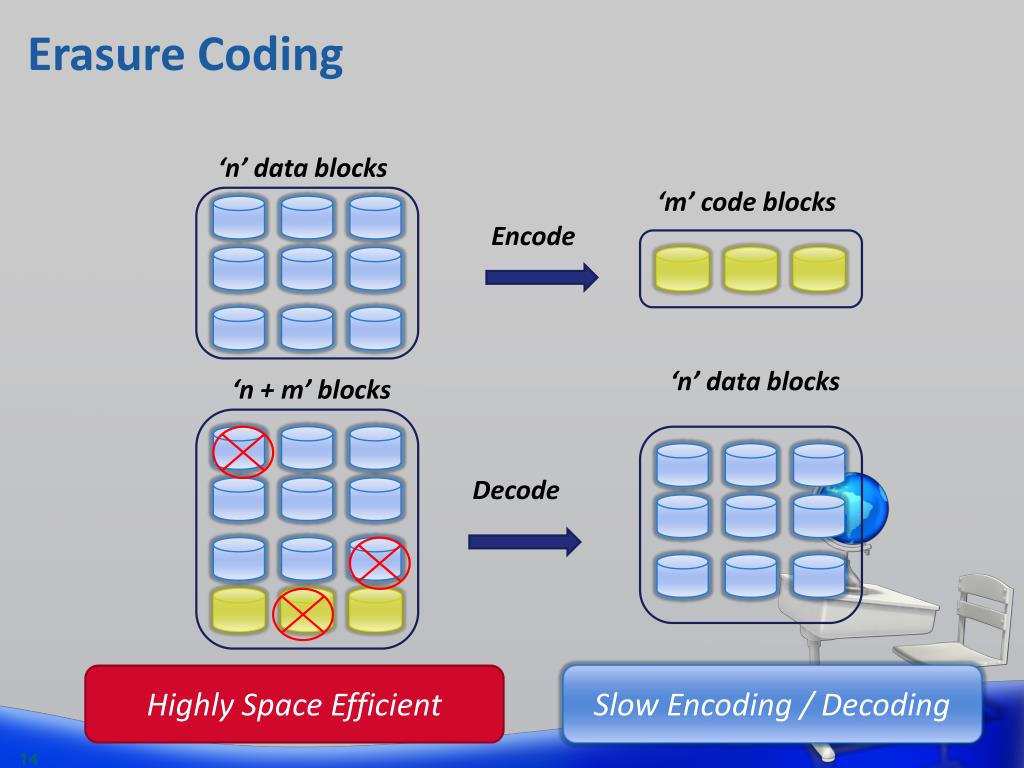
Blocks 1 and 2 contain the user data we want to protect (n = 2), and the third is called a parity block. In a 3,2 encoding, three blocks (m = 3) are spread across three distinct physical devices. Erasure coding explained (examples)Įrasure coding is easiest to understand with examples. So, unlike RAID mirroring which requires a complete second copy, erasure coding allows greater efficiency, requiring just one parity block for every three data blocks (called 3,2 encoding). the Reed-Solomon formula, in this case) to enable regeneration of missing data from pieces of known data (parity blocks).
DUPLICACY ERASURE CODING FULL
Unlike RAID striping or mirroring, erasure coding is scalable protection for massive data storage, far more performant, more configurable, and more space-efficient, allowing clusters unlimited growth while maintaining full data protection and responsiveness.Įrasure coding uses advanced mathematics (i.e. Qumulo Core architecture is built around Qumulo Scalable Block Store (SBS), which is the foundation layer that enables efficient block-based data protection with erasure coding.Įrasure coding is entirely different from RAID and solves RAID’s shortcomings. When considering RAID for storage data protection, RAID can’t do it all and often leads to a difficult choice when building RAID configurations: Should IT admins choose between strong data protection, performance, or better storage efficiency? The answer is they want it all, but RAID can’t deliver. And, in the event of a component failure, rebuild times with RAID can be unacceptably slow, which significantly affects performance for users. However, these more advanced RAID configurations can become extremely complex and difficult to manage and maintain. A common option is RAID 5 or disk striping with parity which improves upon efficiency and read performance over mirroring. Also, mirroring can only handle a single drive failure at a time, which generally isn’t enough protection for many use cases, particularly as cluster sizes increase.īeyond mirroring, the RAID standard offers other configurations to optimize for performance, protection, or both. Since mirroring requires at least one full copy of the data, it is wasteful in terms of the space required for data protection.
Mirroring is simple to implement, but it has some disadvantages. In a RAID 1 mirroring configuration, because each copy resides on a separate disk, data is recoverable from the ‘mirror image’ should the primary disk in a set fail. As its name suggests, mirroring involves recording data simultaneously to two (or more) drives, thereby making identical copies-mirror images, so to speak. The most basic data protection configuration is RAID 1, also called Mirroring. Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) To help explain how erasure coding is superior to other methods of data protection, it helps to understand the various forms of data protection out there as well as their advantages and disadvantages. As we will explain below, erasure coding offers superior data protection to a mirror copy mainly because it doesn’t require a full second copy of the data, yet can restore any missing portion.
DUPLICACY ERASURE CODING SOFTWARE
What is erasure coding?Įrasure Coding is a storage data protection method that leverages advanced mathematics to allow file system software to regenerate missing data using pieces of known data called parity blocks.
But you may be wondering a few things, such as what the heck is erasure coding? How does it compare to RAID and mirroring data protection schemes? And what are the advantages and disadvantages of erasure coding compared to other methods for data protection, like RAID striping and mirroring? These are all important questions that we’ll clear up, putting your enterprise in the best position to keep your data safe.
DUPLICACY ERASURE CODING HOW TO
IT administrators can decide how to strike the right balance between performance and recovery time from physical media failure and the number of concurrent failures they need the system to be able to withstand.Įrasure coding is easiest to understand with examples, which we will discuss in more detail below.

One of the main advantages of erasure coding is the flexibility it offers. Erasure coding (EC) is one of the best-known methods for data protection, due in part to its efficiency, as more of the disk is available for data compared with RAID and mirroring strategies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
